Keywords
Biography
Thanh Nho Do is a Scientia Associate Professor & a Cancer Institute NSW (CINSW) Career Development Fellow at School of Biomedical Engineering, University of New South Wales (UNSW), Sydney. He directs UNSW Medical Robotics Lab. In 2015, he was awarded his PhD degree in Mechanical Engineering (Surgical Robotics) from the School of Mechanical & Aerospace Engineering (MAE), Nanyang Technological University (NTU), Singapore. He also received his...view more
Thanh Nho Do is a Scientia Associate Professor & a Cancer Institute NSW (CINSW) Career Development Fellow at School of Biomedical Engineering, University of New South Wales (UNSW), Sydney. He directs UNSW Medical Robotics Lab. In 2015, he was awarded his PhD degree in Mechanical Engineering (Surgical Robotics) from the School of Mechanical & Aerospace Engineering (MAE), Nanyang Technological University (NTU), Singapore. He also received his B. Eng. degree in Manufacturing Engineering with Honor Program from the Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Ho Chi Minh City University of Technology, Vietnam. He was a Postdoctoral Scholar at California NanoSystems Institute (CNSI), UC Santa Barbara (UCSB), USA. He also worked as a Research Fellow and a Group Leader at Robotic Research Center (RRC), School of Mechanical & Aerospace Engineering (MAE), Nanyang Technological University (NTU), Singapore.
His main research interests include:
- Flexible surgical devices, especially Natural Orifice Transluminal Endoscopic Surgery (NOTES) systems, for gastrointestinal cancer treatments
- Soft robotics including stretchable sensors and actuators for haptic/tactile displays and their applications to other robotic systems
- Soft assistive device for heart failure and soft artificial organs
- Soft Wearable Haptic Devices
- Functional materials for soft electronics and biomedical applications
- Variable stiffness structures for flexible endoscopic systems, soft robotics and other biomedical applications
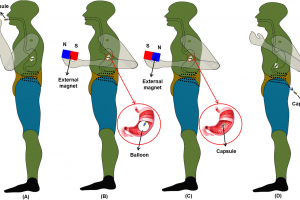
- Miniature soft magnetic robots for drug delivery systems
- Soft magnetic capsule endoscopy for obesity treatments and gastrointestinal diagnosis
- Soft pneumatic/hydraulic actuators
- Soft programmable planar fabric actuators
- Advanced wearable systems for haptic/tactile displays and NOTES systems
- Advanced mechatronic systems for the treatment of tracheal diseases and other respiratory disorders
- Nonlinear backlash/hysteresis modeling and identification methods
- Advanced control algorithms (feedforward and nonlinear adaptive control) for flexible medical systems and smart materials and structures
Editorial Activities:
- Guest editor: Endoscopy, joint collection between Nature communications Engineering, Nature Communications Medicine and Scientific Reports
- Editor-Nature Communications Engineering
- Guest Editor-Sensors, Special Issues "Soft Sensors, Actuators and Sensing Technology for Medical Applications"
- Guest Editor-Micromachines, Special Issues "Soft Robotics: Design, Fabrication, Modeling, Control and Applications"
- Topic Editor-Frontiers in Medical Technology-Diagnostic and Therapeutic Devices, Research Topic "Wearable Soft Robotics in Diagnostics and Therapeutics"
Lab Members and Research Activities:
Please visit UNSW Medical Robotics Lab

Dr. Do is currently looking for undergraduate and postgraduate students to join his research group starting 2026. The research projects include
-
Project 1: The design, fabrication, modeling, control of novel soft artificial organs including soft robotic hearts using soft robotic technologies
-
Project 2: The development of flexible surgical robot for endovascular intervention in circulatory systems and surgical removal of cancers in luminal organs such as lung, pancreas, breast, gastrointestinal tract etc.
- Project 3: The development of flexible surgical robot for eearly detection and surgical removal of cancers in luminal organs (or tubular organs) such as lung, pancreas, breast, gastrointestinal (GI) tract etc.
-
Project 4: Soft wearable haptic devices for VR/AR and medical applications
- Project 5: Soft wearable assistive device for human augmentation
- Project 6: Advanced soft robotic actuators for biomedical applications
Prospective students with background in mechanical design, mechatronics, robotics, control systems, and soft materials with good hands-on skills please feel free to contact Dr. Do to discuss desired projects. Please also include CV and transcript together with names and contacts of at least two academic referees.
There are several scholarships available for both domestic and international students. Please follow the below links for deadlines and other information:
-
Determine Your Eligibility for a Scholarship: https://selfassessment.research.unsw.edu.au/
-
Meet English requirement: https://www.unsw.edu.au/english-requirements-policy
-
Key-dates: https://research.unsw.edu.au/key-dates
-
UNSW Post Graduate Research Scholarship for International Students,
-
UNSW Post Graduate Research Scholarship for Domestic Students
-
Australia Awards and Endeavour Scholarships and Fellowships
-
UNSW/Home Country Joint Scholarship
-
Vietnam-Vingroup Scholarships (for Vietnamese candidates)
My Grants
- 2026-2027: Australia Japan Innovation Fund (Co-CI)
- 2026-2028: Vanguard Grant, Heart Foundation of Australia (Co-CI)
- 2026-2028: 3Rs grant (Co-CI)
- 2025-2030: NHMRC Ideas Grant (Lead CI)
- 2025-2028: Cancer Institute NSW Career Development Fellowship (Sole CI)
- 2025-2028: NSW Cardiovascular Early-Mid Career Researcher Grant (Sole CI)
- 2025-2026: GLOBAL RESEARCH AND IMPACT PROGRAM Grant (Lead CI)
- 2024: UNSW Research Infrastructure Scheme 2024 (Lead CI)
- 2024: UNSW minor equipment grant (Lead CI)
- 2024-2026: 3Rs Grant (Lead CI)
- 2023: GROW Early Career Academics Grant (Sole CI)
- 2023-2024: Faculty of Engineering Goldstar Award Grant (Lead CI)
- 2023-2027: ARC Discovery Project (Co-CI)
- 2022-2026: UNSW Scientia Grant (Sole CI)
- 2022-2032: Google Research Program Project (Sole CI)
- 2022: GROW Early Career Academics Grant (Lead CI)
- 2021-2027: ARC Research Hub for Connected Sensors for Health (Co-CI)
- 2021-2024: Vanguard Grant, Heart Foundation of Australia (Lead CI)
- 2021-2022: 2021 Technology Research Grants, Intuitive Surgical, USA (Lead CI)
- 2021: The Frontiers Technology Clinical Academic Group 2020 Grant (Lead CI)
- 2021: UNSW minor equipment grant (Lead CI)
- 2020: UNSW Research Infrastructure Scheme 2018 (Lead CI)
- 2020: UNSW Research Infrastructure Scheme 2020 (Lead CI)
- 2018-2022: UNSW Start-Up Grant (Sole CI)
- 2018-2022: UNSW Scientia Grant (Sole CI)
- 2018: UNSW minor equipment grant (Lead CI)
- 2018-present: (Sole CI or Co-CI) Generous Supports from the Graduate School of Biomedical Engineering, Faculty of Egnineering, and University of New South Wales etc.
My Awards
- 2026: Ministerial Award for Rising Star in Cardiovascular Research
- 2025: Finalist Best Poster Award, IROS 2025
- 2025: CINSW Career Development Fellow
- 2024: UNSW GRIP Award
- 2024, 2025: World Top 2% Scientist, Stanford University
- 2024: Best Poster Award, IROS 2024
- 2024: WHO's Future Driver in Global Health & 3D Bioprinting
- 2024: NSW Young Tall Poppy Science Award
- 2024: NSW Cardiovascular Research Network (CVRN) Professional Development Award
- 2024: Top 4 Robots of the Year 2023 by Thomson Reuters
- 2023: 2x Finalist Best Poster Awards, EMBC 2023
- 2023: Best Poster Award, EMBC 2023
- 2023: Best Poster Award, ICRA 2023
- 2023: Top 100 in Engineering Scientific Reports
- 2023 UNSW Faculty of Engineering Goldstar Award
- 2022 Google Research Scholar Award
- 2022 NSW Cardiovascular Research Network (CVRN) Professional Development Award
- 2021 Arc PGC Outstanding Supervisor Award
- 2020 The Best of Advanced Materials Technologies
My Teaching
Publications
ORCID as entered in ROS
Videos
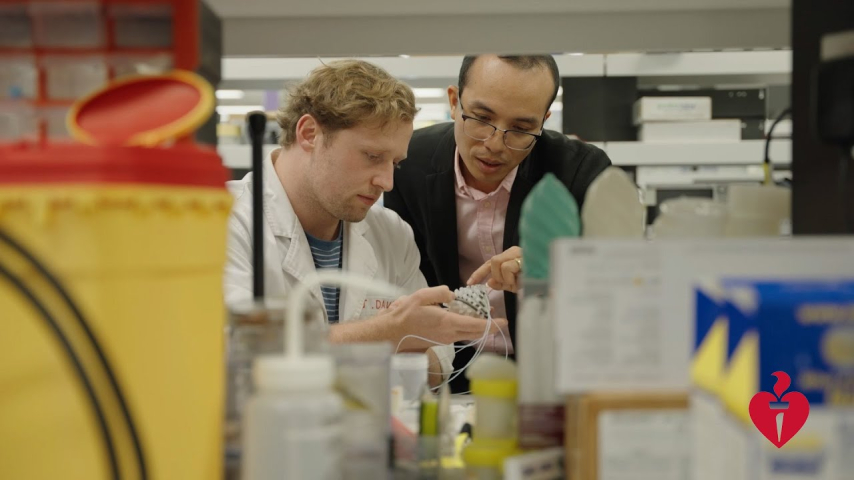
Dr Do and his team are working on a soft robotic device to improve how a failing heart pumps blood. Their aim is to make it less bulky and more portable than the LVAD – and more cost-effective. This will make it easier for more people around Australia to access.
This exciting research could give people waiting for a heart transplant more time and help improve their quality of life.
And it’s because of you that ground-breaking research like Dr Do’s is possible. Will you help advance cardiovascular research and give the gift of life today?
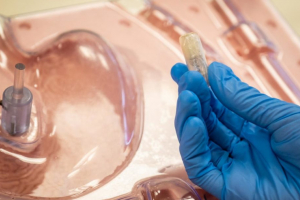
3D bioprinting is a process where natural tissue-like structures are printed using living cells and other natural tissues known as "bio-ink", in order to repair organ or tissue damage or ruptured blood vessels.
The use of living cells in the printing process allows these man-made structures to fuse naturally with the human body and continue to grow.
Currently, biomaterials must be created outside of the body before relying on typically invasive surgery to insert the materials inside the body, which can lead to high blood loss, infections, and other complications.
Team leader Thanh Nho Do said this new device, named F3DB, will eliminate those complications and risks by printing directly inside the body.
"Currently no commercially available technology can perform direct 3D printing inside the human body," Do told Reuters.
F3DB features a three-axis printing head that can bend and twist using hydraulics on the tip of a soft robotic arm. The printing nozzle can print pre-programmed shapes or can be operated manually if more complex or undetermined printing is required.
The smallest prototype has a diameter of approximately 11-13 millimetres (mm), similar to a commercial endoscope, but it could be scaled even smaller in the future.
"Soft robots (are) very good for working with the human body," Do, the director of the University of New South Wales Medical Robotics Lab, said.
"They can offer high flexibility and adaptability. This means they can fit to any area inside the human body."
Do believes that the device is on track for commercialisation in the next five to seven years, pending further clinical trials.