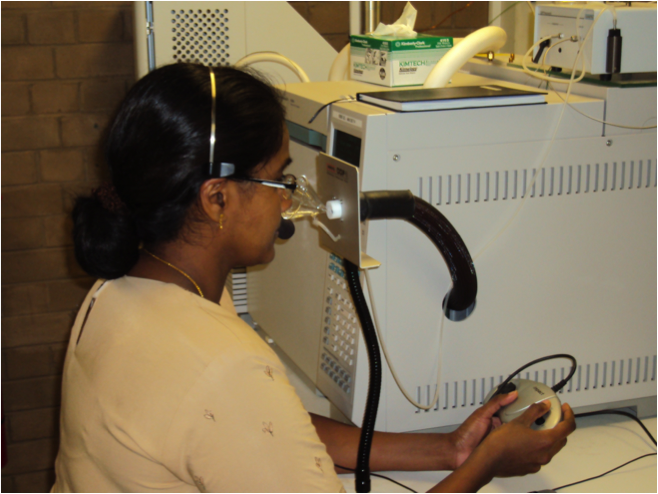
Burden of cancer – prevention, treatment, costs and related diseases
Field of Research (FoR):
SEO tags:
Field of Research (FoR):
SEO tags:
The aims of this Fellowship are to utilise and further extend recently developed methods for estimating different aspects of disease burden in order to:
Indigenous Australians with Mental Health Disorders and Cognitive Disabilities in the Criminal Justice System
High rates of Indigenous Australians with mental health disorders and cognitive disabilities in the criminal justice system are evidenced in a current ARC Linkage project.
University student travel-health and immunity study
Field of Research (FoR):
SEO tags:
Field of Research (FoR):
SEO tags:
The congregation of students, who may have similar infectious diseases risks, may amplify infectious disease outbreaks, as seen in the USA. In contrast to the USA, there are no existing requirements at universities in Australia regarding proof of immunisation.
Olfactory Characterisation of Odours for Optimising Impact Assessment
Field of Research (FoR):
SEO tags:
Field of Research (FoR):
SEO tags:
Complaints due to odour annoyance have become a major issue for intensive livestock, waste management and wastewater treatment operators.
Fundamental investigation of particle-fluid flow in IsaMill
Field of Research (FoR):
SEO tags:
Field of Research (FoR):
SEO tags:
The Australian mining and minerals processing industries generated exports of around $56 billion in 2004/5, representing approximately 44 per cent of Australia?s total exports. Grinding is one of basic operations in minerals processing, liberating valuables from the host rock.
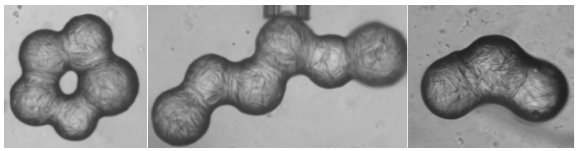
Ice Cream Meltdown
Field of Research (FoR):
Field of Research (FoR):
Everyone has experienced the sadness associated with melting ice cream, but there are actually some fascinating physics at work that determine the time it takes for a block of ice cream to melt and collapse under its own weight.
Measuring Asian Art's Contribution to Contemporary Culture
Field of Research (FoR):
SEO tags:
Field of Research (FoR):
SEO tags:
Through the development of an innovative methodology combining art theory and curatorial practice, this project provides comprehensive analysis of the role played by Asian (and Australian) visual art in understanding how places and communities are transformed by the impact of immigration/migratio
Practical Aesthetics: A Study in Understanding Real Events through Contemporary Art
Field of Research (FoR):
SEO tags:
Field of Research (FoR):
SEO tags:
Funded by an Australian Research Council ARC Discovery grant, this project establishes the significance and value of art concerned with social and political events, providing the first comprehensive analysis of the treatment of real events in art since the watershed of September 11, 2001.
Models to inform prevention and control of emerging infectious diseases in real time
Field of Research (FoR):
SEO tags:
Field of Research (FoR):
SEO tags:
This proposed research addresses the need for real-time tracking of emerging infectious diseases, both spatially and temporally, to inform international and national outbreak response teams, aid in the implementation of real-time containment strategies and ultimately the timely control of emergin
Modulation of Gap Junction Channels for the Treatment of Spinal Cord Injury
Field of Research (FoR):
Field of Research (FoR):
This research grant is a trans-Tasman collabo
Travellers visiting friends and relatives: new approaches to understanding and reducing infectious disease risks
Field of Research (FoR):
SEO tags:
Field of Research (FoR):
SEO tags:
This research will investigate the contribution to the burden of infectious diseases in Australia from travel by migrant Australians who visit friends and relatives in their country of birth.
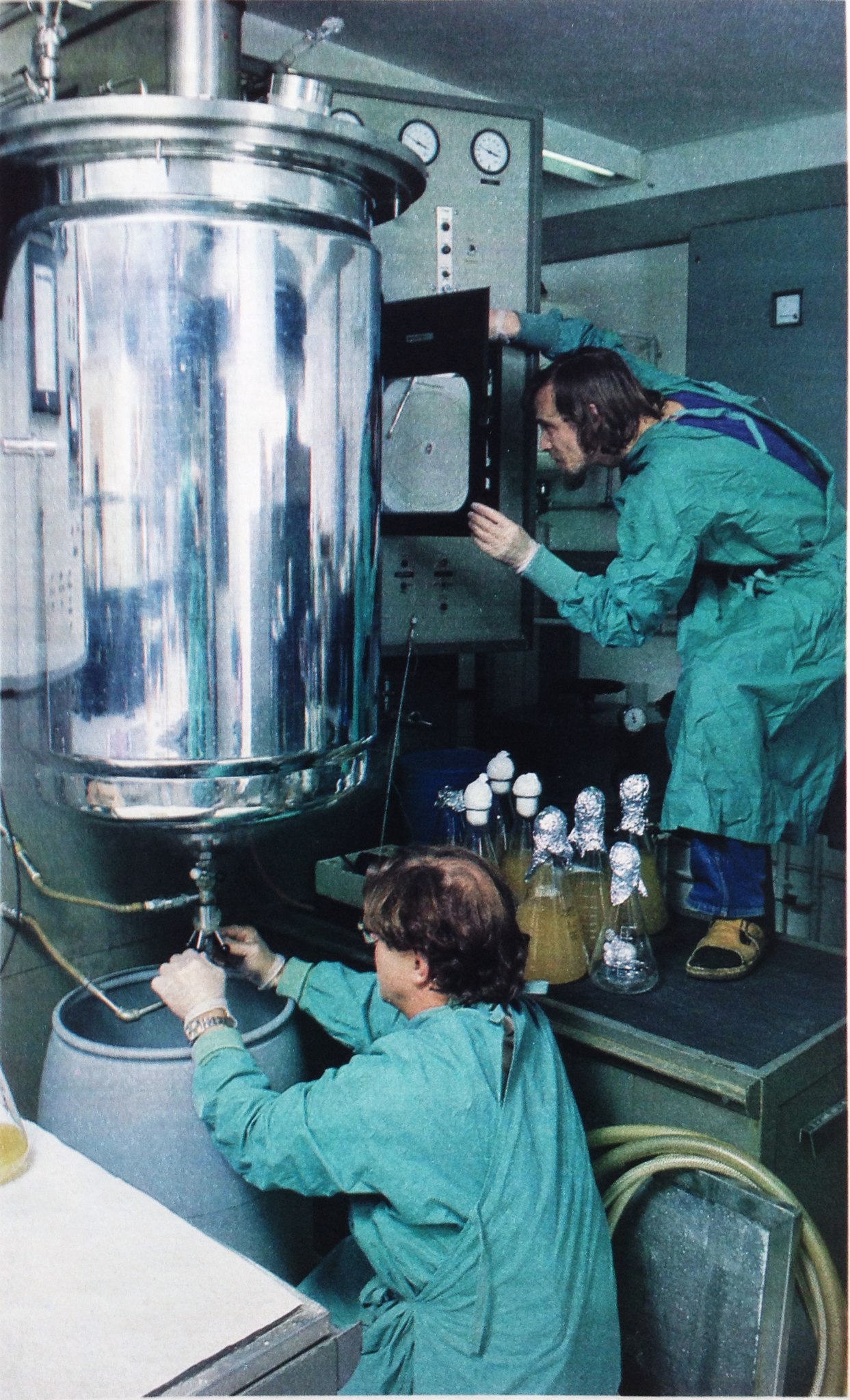
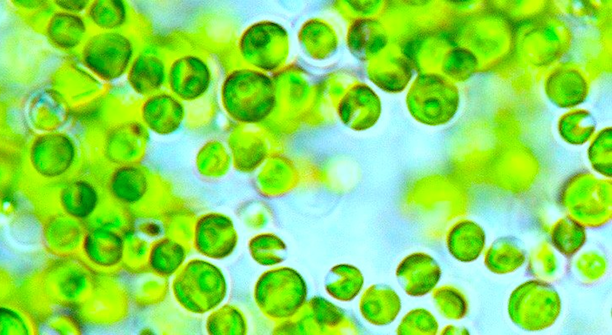
Advanced Nanomaterial for Harvesting and Processing of Microalgae
Field of Research (FoR):
Field of Research (FoR):
A research opportunity exists for undergraduate and higher degree research student in science and engineering to investigate the use of advanced nanomaterials for microalgae harvesting and processing at UNSW's School of Chemical Engineering.
Nanostructured Particle Formation during Fat Digestion and Drug Delivery
Field of Research (FoR):
Field of Research (FoR):
We have a number of possible projects in this area dealing with the fascinating self-assembly of monoglycerides in water, as occurs whenever we ingest and digest fats.
The Cold War Obesity Crisis: Fatness, Public Health, and Medical Science in the United States, 1940-1970
Field of Research (FoR):
SEO tags:
Field of Research (FoR):
SEO tags:
In 1951 the US Public Health Service declared obesity, newly reinterpreted as an addictive disorder, to be the nation’s leading health problem.
Public and Proprietary Knowledge in Biotechnology: An Historical and Sociological Analysis of First Generation Recombinant DNA Pharmaceuticals Development
Field of Research (FoR):
SEO tags:
Field of Research (FoR):
SEO tags:
In the 1980s many scientists joined commercial genetic engineering ventures.
Food Emulsion Microstructure and Shape Effects
Field of Research (FoR):
Field of Research (FoR):
The stability of many foods is based on, or affected by, emulsions arrested by colloids. Prediction, and thus optimization, of these products’ stability is often impossible because practitioners lack the fundamental understanding needed to design microstructural and rheological properties.
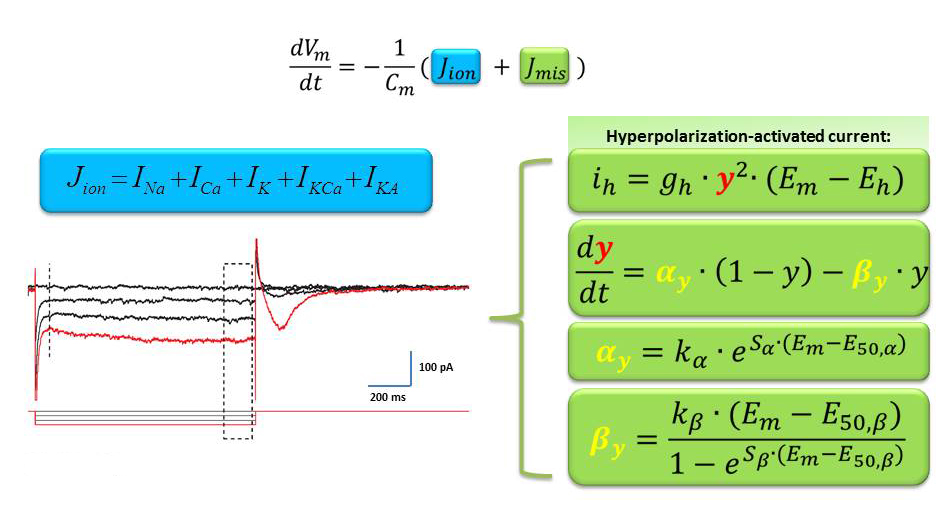
Large-Scale Parameter Optimisation of Ionic Cell Models
Field of Research (FoR):
SEO tags:
Field of Research (FoR):
SEO tags:
Biological systems models typically contain many parameters, many of which are hidden and cannot be determined experimentally in the same system.
Modelling Markup Language Representation for Biological Tissues
Field of Research (FoR):
SEO tags:
Field of Research (FoR):
SEO tags:
Anatomically-accurate model of rabbit cardiac pacemaker tissue defined using the MML framework, illustrating a propagating electrical wavefront emanating from the central pacemaking site.
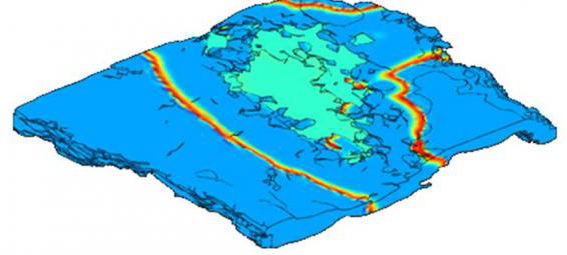
Modelling of Retinal Electric Stimulation
Field of Research (FoR):
SEO tags:
Field of Research (FoR):
SEO tags:
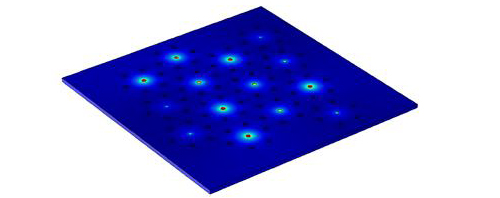
Electric potential profile generated by retinal implant 98-electrode array
Modelling Cardiovascular–Rotary Blood Pump Interactions
Field of Research (FoR):
SEO tags:
Field of Research (FoR):
SEO tags:
Simplified fluid-structure interaction model of ventricular assist flow in the presence of contracting heart wall and aortic valve leaflets. Ventricular inlet (left) and outlet (right) boundaries are shown as white squares, and ventricular assist flow occurs through the outlet at the bottom.
Modelling Brain Activation In Electroconvulsive Therapy
Field of Research (FoR):
SEO tags:
Field of Research (FoR):
SEO tags:
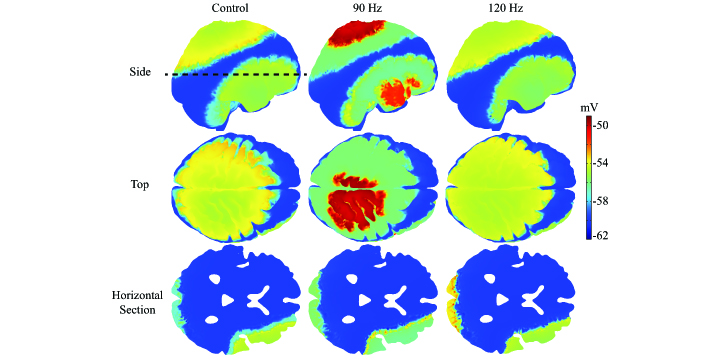
Simulated brain activation during electroconvulsive therapy.
Associate Professor Paul Hagan's CV
Field of Research (FoR):
Field of Research (FoR):
Take a closer look at Associate Professor Paul Hagan's CV
Political Institutions, War & Peace: Global and Regional Dynamics
Field of Research (FoR):
SEO tags:
Field of Research (FoR):
SEO tags: